Java Linked List Algorithm Example
Java Linked List Algorithm Example. Linked list can be an underlying data structure to implement stack, queue or sorted list. //if list is empty, head and tail points to newnode.
We first initialize ptr with the address of head. //create addnewnode () method to add a node into a list. //add a node to the list public void addnode(int item) { //create a new node node newnode = new node(item);
Class Main { Public Static Void Main(String[] Args) { // Creating A Linked List Linkedlist Animals = New Linkedlist<>();
Class doublylinkedlist { //a node class for doubly linked list class node{ int item; For example, the insertion operation adds a new element to the linked list. Arraylist is an resizeable array implementation of list interface.
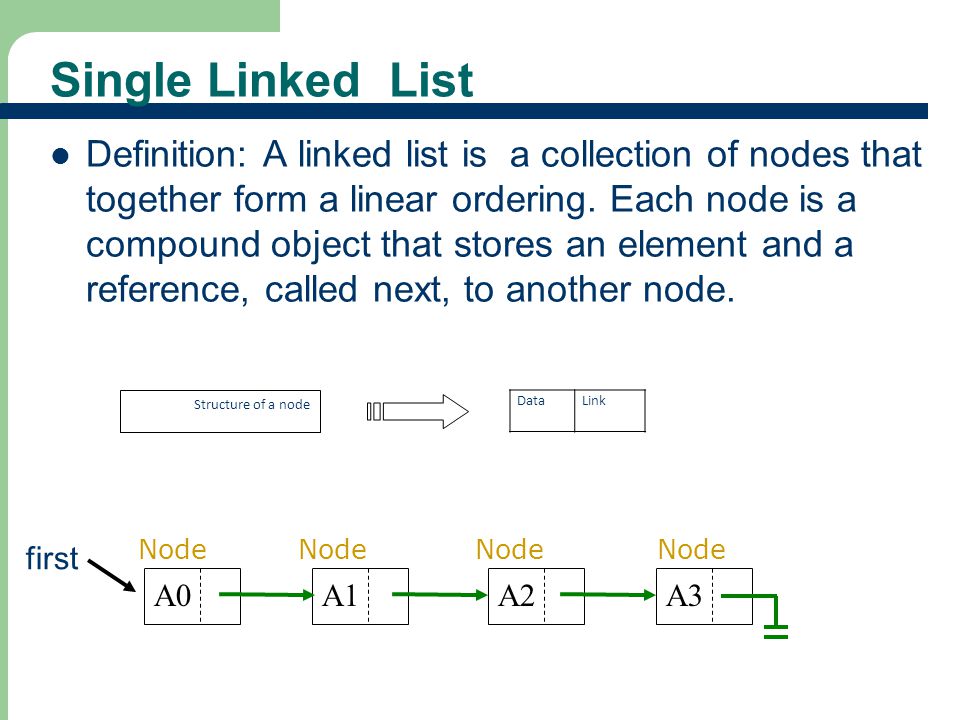
Firstly, A Linked List Is A Collection Of Things Known As Nodes That Are Kept In Memory At Random.
//tail points back to head tail.next = head; Public void addnewnode (string data) {. //the newnode is pointed by both head or tail.
//Push Root Node To The Stack Int A = 0;
The diagram shown below depicts a circular linked list. These constructors will simplify a number of the algorithms below. Public class main { public static void main (string [] args) throws ioexception { bufferedreader br = new bufferedreader (new inputstreamreader (system.in));
Secondly, A Node Has Two Fields:
} } //display the nodes in circular linked list public void displaylist() { node current = head; Now the ptr points to the first node of the linked list. So, in this list, a is pointing to b, b is pointing to c and c is pointing to d but.
For (Int I = 0;
For example, to create a list with one element containing the item 5, we could write: Stack < integer > stack = new stack <>(); Public class main { public static void main(string[] args) { linkedlist cars = new linkedlist();
Komentar
Posting Komentar